APCSA Vocab
Week 1
- Objects have attributes which are characteristics of an object
- A class is the blueprint that objects are created from. Instantiating an object calls the constrcutor to create an object.
-
A constructor is code that has the same name as the class and tells the computer how to create a new object
- Parameter: a variable in the method/constructor signature that defines the type of value to receive when the method or constructor is called
- in the definition of a function
- Argument: a value passed to a method/constructor when the method or constructor is called
- when calling the function
# Collegeboard Unit Lessons
Unit Lesson Notes from Class Presentations
- toc: true
- badges: true
- comments: true
- categories: [jupyter]
- image: images/acorn.png
Unit 1: Primitive Types
- Primitives Example:
- Primitive Types
- Boolean
- Numeric
- Character
- char
- Integral
- Integer
- byte
- short
- int
- long
- FLoating-point
- float
- double
- Integer
- Character
- Wrapper Classes (Non-Primitive)
- String, Array, etc.
- Like an object so has methods
- Additional W1 Notes:
- Input
Scanner input;input = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("Enter an integer: ");input.close();
- Output
System.out.println();Unit 2: Using Objects
Unit 3: Booleans Expressions and if Statements
- Input
Compound Boolean Expressions
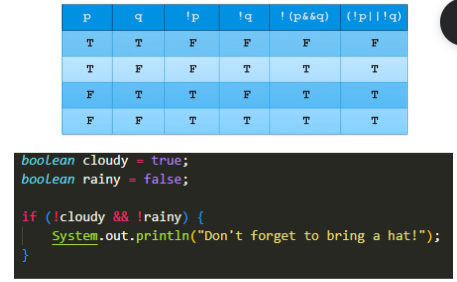
- De Morgan’s Law - helps simplify boolean expressions
!(a&&b)= (!a || !b)- Truth tables to visualize Boolean identities
Comparing Objects
- use
==to see if two obj references are aliases for the same obj or to see if an obj is null - use
.equals()to see if the attributes of two obj are the sameUnit 4: Iteration
While Loops
- do something while a condition is true
int x = 5;
// The boolean expression in this case is x > 0 while (x > 0) { System.out.println(x); x–; }
- while loops can be used to iterate over elements int[] array = {3, 7, 0, 2, 4, 5, 9, 1, 3, 6, 3}; int total = 0; int i = 0;
while (i < array.length) { total += array[i]; i++; }
System.out.println(total);
- infinite while loops - run over and over permanently since boolean condition true at all times import java.util.Scanner;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String choice;
while (true) { System.out.println(“Would you like to continue: “); choice = input.nextLine(); if (choice.equals(“No”)) { break; } }
Unit 5 Writing Classes
- Class - blueprint to create objects
- instance variables/attributes (data)
- constructors
- methods
- accessors/getters
- mutators/setters
- main method (tester)
- Objects are instances of a class
- Methods are what an object can do
publicmeans it can be accessed outside the classprivatemeans its restricted to accessing it inside the class- Constructors
- initialize instance variables when an object is created public class Cow {
// instance variables private String cowType; private String sound; private int numMilkings;
// constructor public Cow (String cowType, String sound){ this.numMilkings = 0; this.cowType = cowType; this.sound = sound; }
public String getSound(){ return sound; } }
public class CowDriver{ public static void main(String[] args) { Cow myCow = new Cow(“holstein”, “moo”); System.out.println(myCow.getSound()); // myCow.sound = “bark!”; } }
CowDriver.main(null); public class Song {
/** Verse - prints out a verse of the song
- @param number - a String like “one”, “two”, etc.
- @param rhyme - a String like “thumb”, “shoe”, etc. */ public void verse(String number, String rhyme) { System.out.println(“This old man, he played “ + number); System.out.println(“He played knick knack on my “ + rhyme); }
// The chorus method public void chorus() { System.out.println(“With a knick knack paddy whack, give a dog a bone.”); System.out.println(“This old man came rolling home.”); }
public static void main(String args[]) { Song mySong = new Song(); mySong.verse(“one”, “thumb”); mySong.chorus(); mySong.verse(“two”, “shoe”); mySong.chorus(); mySong.verse(“three”, “knee”); mySong.chorus(); mySong.verse(“four”, “door”); mySong.chorus(); } }
Song.main(null);
Unit 6 Arrays
- Arrays Team Lesson
- Traversing Arrays 6.2
- Team Lesson